

Custom Java settings
|
NOTE
In order for the ADPS version 1.1.0.b2 components to work correctly with a custom JDK, complete the steps below.
|
Create a script to set JAVA_HOME
-
Create a new script in the etc/profile.d catalog, e.g. etc/profile.d/set_java_home.sh. You can use a text editor to do so.
$ sudo vi /etc/profile.d/set_java_home.sh -
Add the following lines to the file:
#!/bin/bash export JAVA_HOME=<jdk_path> export PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/binwhere
<jdk_path>is the path to your custom JDK. -
Make the script executable.
$ sudo chmod +x /etc/profile.d/set_java_home.sh -
To apply the changes, restart the system or run the
sourcecommand for your script in all active sessions.$ source /etc/profile.d/set_java_home.sh -
After you’ve applied the changes, it’s recommended to check Java installation by running the commands below to determine that the correct Java version is used:
$ java -version $ javac -version
Create a symlink to unify the path to JDK
-
Open the console on each server where the ADPS components are installed (or where you plan to install them).
-
Run the following command to create a symbolic link from a custom JDK path to the standard path that is expected by bigtop:
$ if [ -e /usr/java/jdk1.8 ] || [ -L /usr/java/jdk1.8 ]; then echo "File or symlink already exists at /usr/java/jdk1.8" else sudo ln -s <jdk_path> /usr/java/jdk1.8 echo "Symlink created successfully" fi
Change the path to cacerts:
-
In ADCM, enter the ADPS cluster configuration and enable the Show advanced flag.
-
Expand the Advanced SSL configuration parameter group.
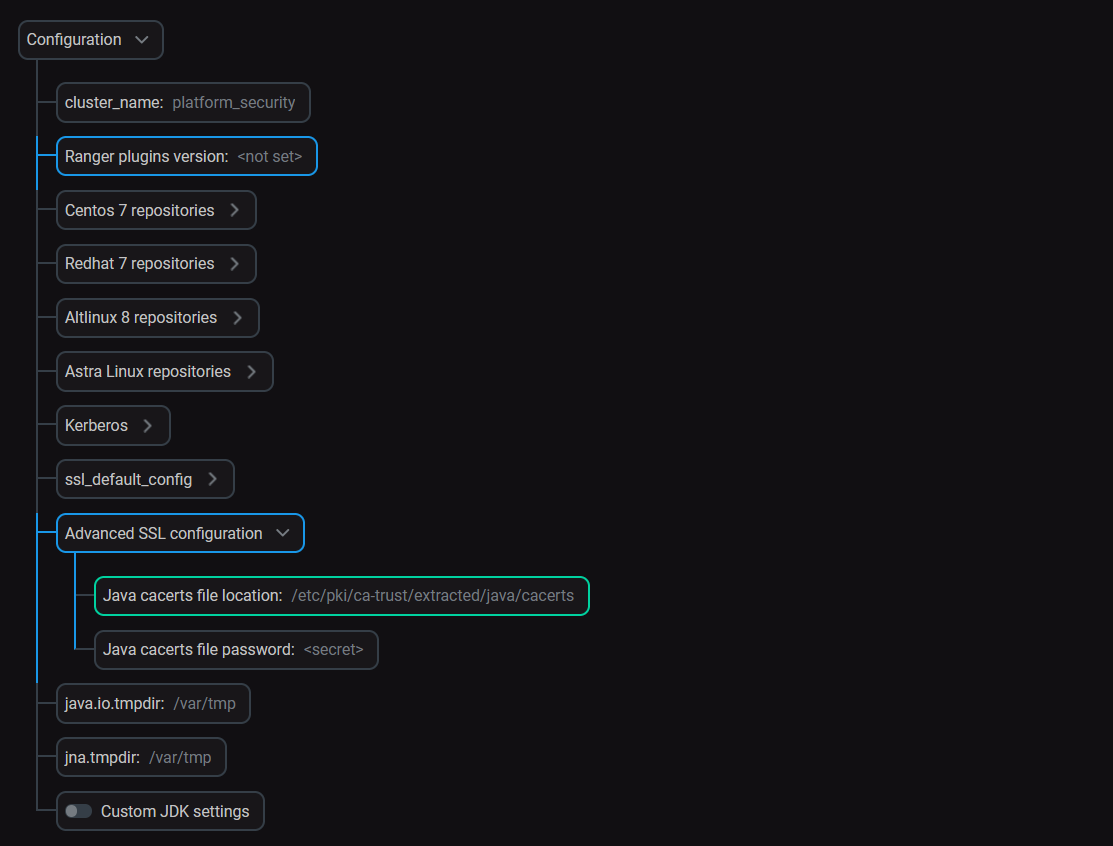 Advanced SSL configuration parameters
Advanced SSL configuration parameters -
Change the Java cacerts file location parameter to the cacerts file path that your custom Java uses.
Configure alternatives (AltLinux)
If you use the alternatives in AltLinux, complete the steps below:
-
Create a configuration file in /etc/alternatives/packages.d. For example:
$ sudo vim /etc/alternatives/packages.d/zulu-8 -
Add the following lines to the file:
/usr/bin/java /usr/lib/jvm/zulu-8/jre/bin/java 1800340 /usr/bin/jjs /usr/lib/jvm/zulu-8/jre/bin/jjs /usr/lib/jvm/zulu-8/jre/bin/java /usr/bin/keytool /usr/lib/jvm/zulu-8/jre/bin/keytool /usr/lib/jvm/zulu-8/jre/bin/java /usr/bin/policytool /usr/lib/jvm/zulu-8/jre/bin/policytool /usr/lib/jvm/zulu-8/jre/bin/java /usr/bin/servertool /usr/lib/jvm/zulu-8/jre/bin/servertool /usr/lib/jvm/zulu-8/jre/bin/java /usr/bin/pack200 /usr/lib/jvm/zulu-8/jre/bin/pack200 /usr/lib/jvm/zulu-8/jre/bin/java /usr/bin/unpack200 /usr/lib/jvm/zulu-8/jre/bin/unpack200 /usr/lib/jvm/zulu-8/jre/bin/java /usr/bin/orbd /usr/lib/jvm/zulu-8/jre/bin/orbd /usr/lib/jvm/zulu-8/jre/bin/java /usr/bin/rmid /usr/lib/jvm/zulu-8/jre/bin/rmid /usr/lib/jvm/zulu-8/jre/bin/java /usr/bin/rmiregistry /usr/lib/jvm/zulu-8/jre/bin/rmiregistry /usr/lib/jvm/zulu-8/jre/bin/java /usr/bin/tnameserv /usr/lib/jvm/zulu-8/jre/bin/tnameserv /usr/lib/jvm/zulu-8/jre/bin/java /usr/lib/jvm/jre /usr/lib/jvm/zulu-8/jre /usr/lib/jvm/zulu-8/jre/bin/java alternatives-update
-
Update the alternatives system.
$ sudo alternatives-update -
Check the settings. If everything was done correctly, it will allow the system to correctly manage the connections and versions of various Java executables.